Robots, Analytics, And The Future Of Healthcare Delivery
By Andy Dé, Alteryx

Last week, the world media confirmed the number of coronavirus infections had surpassed 27 million cases worldwide, with deaths hitting nearly 900,000, nearly 187,000 of which occurred here in the U.S. The pandemic has not only upended life, economies, and industries, it has been the single largest disruptor for the healthcare industry globally, triggering unprecedented transformation.
COVID-19 has rapidly accelerated healthcare’s already growing dependence on data-driven technologies. Without data insights, the care system would have unquestionably been brought to its knees. The outbreak and the resulting supply chain disruption immediately triggered a massive shortage of N-95 masks, gloves, and PPE. The financial crisis resulting from the loss of elective procedures impacted revenue and margins while creating unprecedented risks for the health and safety of caregivers. All these factors have driven swift digital transformation and new kinds of digital patient engagement.
Perhaps the most significant areas of transformation are the underlying clinical processes for patient engagement, diagnosis, and post-discharge patient care, many of which are being driven by AI and analytics-enabled robotics. This means that technologies like machine learning, robotics, machine vision, and exoskeletons will be at the forefront of delivering a new kind of healthcare.
How Can Healthcare Innovation Leaders Embrace Robotics?
I’ve attempted to lay out four primary areas, and 14 key applications that will be enabled by robotics in the post-pandemic healthcare provision, many of which are already in use across the world at this time. I hope this will provide a useful foundational overview of how data, AI, and robotics are creating the future of healthcare provision.
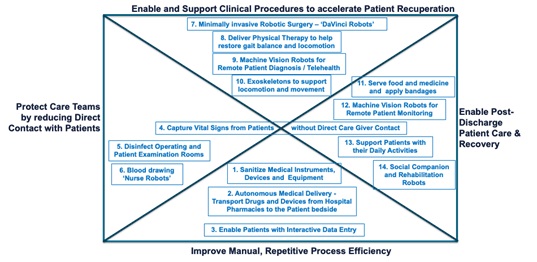
Figure 1. Strategy Framework articulating the Deployment of Medical Robots in the post-Pandemic “New Normal”. Copyright Andy De (2020). All right reserved.
Improving the efficiency of repetitive manual processes
- Sanitizing Medical Instruments, Devices and Equipment
Sanitization is prone to human error and can create risks for hospital employees and patients alike. Therefore, these tasks are a no-brainer for automation, using sophisticated “pick and place” robots to disinfect thousands of medical instruments, devices, and equipment, with consistency and without fatigue.
- Autonomous Delivery
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) have already been deployed in hospitals in Germany and other European countries, allowing the automatic pick-up and delivery of a multitude of critical items, including drugs, devices, patient samples, meals, waste, and ward linens. At the Mongkutwattana General Hospital in Bangkok, robot nurses are used to dispense medication and make deliveries throughout the hospital. These AGV robots can even take the elevators by themselves and communicate in both Thai and Chinese.
- Interactive Data Entry
Data entry from paper-based forms creates several challenges, especially for seniors and the disabled. That’s why robots -- equipped with machine vision – could soon be widely deployed to engage with these patients and capture their information via interactive voice response (IVR) and enter it into digital forms integrated with existing ADT and Patient Portals.
Protecting care teams by reducing direct contact with patients
- Capturing Vital Signs from Patients
Vital signs are perhaps the single largest area in which we’ll see widescale adoption of robotics. Temperature, blood pressure, sugar levels, and pulse oximetry could all soon be captured without contact – indeed, this is already happening in countries like China, Taiwan, and Japan. It is likely we also will see significant adoption in the U.S. soon. This could even extend to robots scanning members of the public for COVID-19 at hospital receptions, retail stores, airline security checkpoints, and even company offices.
- Disinfecting Operating and Examination Rooms
The disinfection process can pose risks to hospital personnel that could easily be mitigated with the use of specialized robots utilizing machine vision and UV light to thoroughly disinfect operating, patient examination, and observation rooms. Using this equipment to clean consistently and with precision could minimize sometimes deadly hospital acquired infections (HAIs).
- Drawing Blood
While it might be hard to envision, robot nurses will help reduce the risks associated with drawing blood for both patients and nurses simply by eliminating the need for the close person-to-person proximity. Companies like Accuvein are already supplying blood-drawing robots to hospitals in the U.S.
Enabling and supporting clinical procedures to accelerate patient recuperation
- Conducting Minimally Invasive Surgery
Though many interventions involving complex procedures or invasive surgeries will continue to be carried out in person, there is significant innovation underway to enable minimally invasive robotic surgeries. Ultimately, these AI-driven surgeries would offer benefits like smaller incisions and scars, reduced infection risk, less need for blood transfusions, faster recovery times and shorter hospital stays.
- Delivering Physical Therapy
Physical therapy for gait, balance, and locomotion is a particularly compelling arena of robotic innovation at this time. Patients with relevant issues can be connected to robots which help them walk, improve their motor skills, and eventually to improve their quality of life.
- Telehealth and Remote Patient Diagnosis
While still a rarity, this is an obvious area for innovation. Given sophisticated machine vision technologies have already been successfully deployed for minimally invasive surgeries, it is a fairly intuitive step to have robotics with similar capabilities for initial diagnosis via telehealth. This would be especially useful for patients located in rural areas who cannot see their doctors in-person often, and is available today from companies like Anybots.
- Exoskeletons
Assisting with post-discharge patient care and recovery
- Serving Food, Medicine, and Applying Bandages
At the Stanley Medical College and Hospital in Chennai, India, a robot named ‘Zafi’, can be seen around the wards serving food, water, and medicine to COVID-19 patients. We’re likely to see more of this, not only across Asia but also in the U.S., Canada, and Europe, given the obvious cost-benefits plus the reduced risk of exposure for nurses and caregivers.
- Remote Patient Monitoring
Given the new reliance on remote patient monitoring (RPM) systems in the wake of the pandemic, the natural next step may be to have fully-connected robots equipped with a speaker, camera, and video screen. These could be deployed at home or skilled nursing facilities to engage and monitor high-risk patients with multiple morbidities, monitor their vital signs, and make sure they’re taking medication.
- Supporting Daily Activities
For seniors in long-term care settings robots like Sam, a robotic concierge manufactured by Luvozo can improve quality of life. Deployed in a senior living community in Washington DC, Sam provides frequent check-ins on seniors and contributes to improved care and lower costs, while improving patient satisfaction.
- Companionship and Rehabilitation
Increasingly, AI-enabled human or animal-resembling robots being equipped with touch sensors, cameras, and microphones that allow them to engage in limited conversation with dependent humans. At present, they’re mostly used to remind patients to check their vital signs and take medications on time, but the PARO Therapeutic robot is an interactive device that looks like a baby harbor seal and is designed to provide the benefits of animal therapy without relying on live animals to alleviate patient stress.
Healthcare is still a new and exciting frontier for robotics, AI, data, and analytics. COVID-19 has been a significant catalyst, hastening the adoption of transformative technologies, many of which work to protect doctors, nurses, caregivers, and first responders. Though this rundown is not exhaustive by any stretch, it does aim to articulate a strategic consideration framework for the use of robotic technologies and envision how they might be used to drive superior business, clinical, population, and patient outcomes beyond the pandemic.
About The Author
Andy Dé is the senior director for healthcare solutions strategy and go-to-market (GTM) at Alteryx. In this role, he leads the innovation, thought leadership, evangelism, go-to-market, and commercialization strategy, planning, and execution for Alteryx’s solutions targeted at healthcare providers and payers. He has over 20 years of prior enterprise software innovation strategy, solutions portfolio management, and go-to-market strategy, planning and execution leadership experience at GE Healthcare, SAP Health-Sciences and Tableau Software.
